What Is Web ;layer Buisness Logic Layer And Data Layer
Reading fourth dimension: eight minutes
When building a spider web application, at that place are three main principles to bear in mind. From a customer's signal of view, the application should be elementary, aesthetically pleasing, and address most of their problems. From the business aspect, a web awarding should stay aligned with its product/market fit. From a software engineer'due south perspective, a web application should be scalable, functional, and able to withstand high traffic loads.
All these bug are addressed in the spider web awarding's architecture. We'll cover the basic concepts of any mod spider web application and explain how the architecture patterns may differ depending on the application you're building.
What is Web Application Architecture?
And so, what is a spider web application and how is it different from a website?
The basic definition of a spider web application is a program that runs on a browser. It's not a website, only the line between the two is fuzzy. To differentiate a spider web awarding from a website, think these iii formal characteristics. A web application:
- addresses a particular problem, even if it's simply finding some information
- is as interactive every bit a desktop application
- has a Content Management System
A website is traditionally understood to simply be a combination of static pages. But today, most websites consist of both static and dynamic pages, which makes almost all modernistic websites – you guessed information technology! – spider web applications. In this commodity, we will utilise the terms interchangeably.
Your figurer, or smartphone, or whatsoever other device you're browsing with is called a client. The other half of the web equation is called a server considering information technology serves you the data you asking. Their communication is called a customer-server model, whose chief business organization is receiving your request and delivering the response back.
Web application architecture is a mechanism that determines how application components communicate with each other. Or, in other words, the way the customer and the server are connected is established by web awarding architecture.
Web applications of different sizes and complexity levels all follow the aforementioned architectural principle, but details may differ. We will further explicate how a basic request-response process works and what components comprise the architecture.
How does the web request work?
To sympathise the components of spider web application compages, nosotros need to understand how they are used in performing the most basic action – receiving and responding to a spider web request.
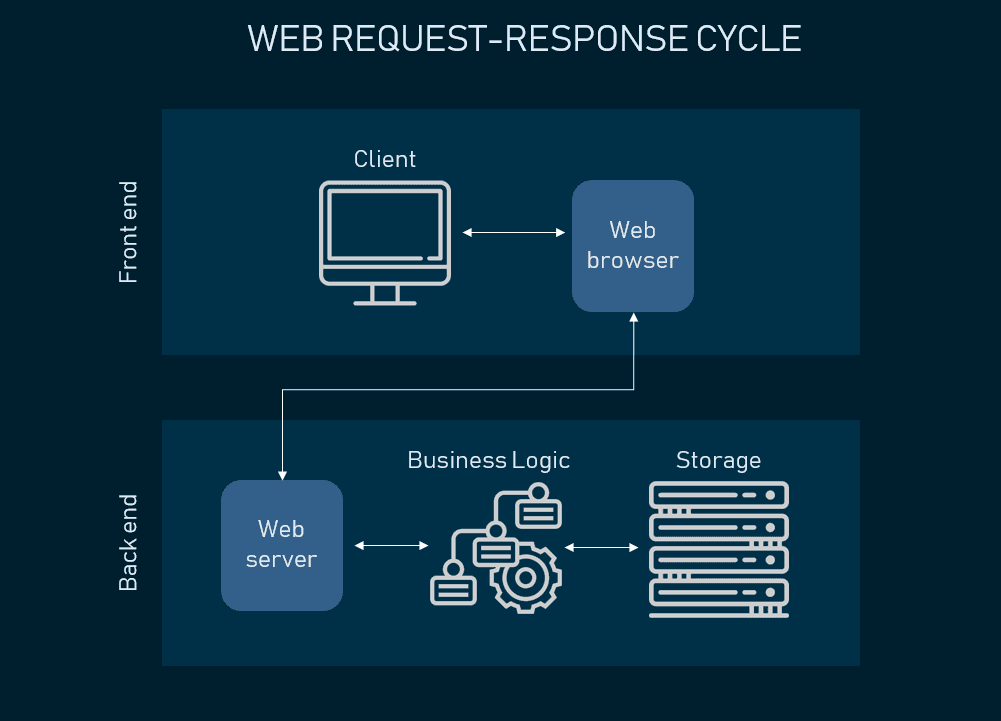
Web request-response cycle
Permit'due south look at Amazon.com to illustrate our explanation.
Showtime, y'all visit amazon.com. Y'all type in the URL and as y'all hit Enter, your browser prepares to recognize this URL, because information technology needs to know the accost of the server where the page is located. So it sends your request to the Domain Name Center (DNS), a repository of domain names and their IP addresses. If you've already visited Amazon from the aforementioned browser, information technology will pull the accost from the cache. So, a browser sends the request to the found IP address using the HTTPS protocol.
Second, the spider web server processes the request. The web server where Amazon.com is located catches the asking and sends it to the storage area to locate the page and all data that follows with it. Just its road is held via Concern Logic (also called Domain Logic and Application Logic). BL manages how each piece of data is accessed and determines this workflow specifically for each application . Every bit BL processes the request, it sends it to storage to locate the looked-for information.
3rd, you receive your data. Your response travels back to you lot and y'all see the content of the web page on your brandish. The graphical interface you see when scrolling Amazon'southward or whatsoever other website is called the front end stop of an application – it depicts all UX and UI components so that a user can access the information they came looking for.
Web awarding architecture components and Three-Tier Architecture
Well-nigh web applications are developed past separating its main functions into layers, or tiers. This allows you to easily supercede and upgrade each layer independently. This architectural pattern is called Multi- or Three-Tier Architecture.
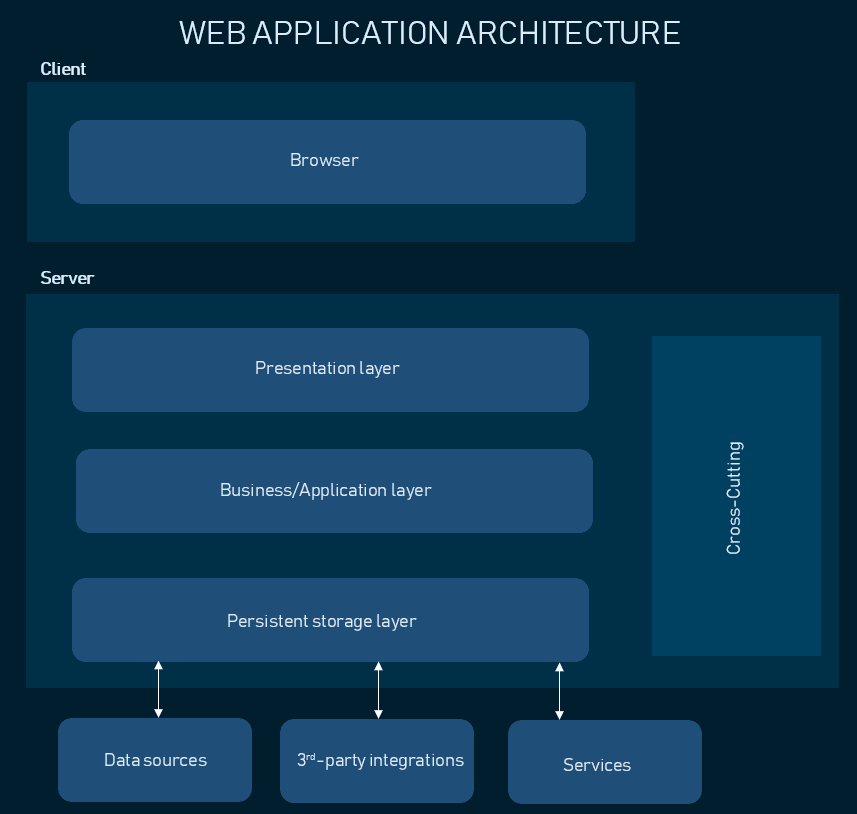
Spider web awarding architecture following the iii-tier pattern
Presentation layer
The presentation layer is attainable to users via a browser and consists of user interface components and UI process components that support interaction with the arrangement. It's adult using three core technologies: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. While HTML is the code that determines what your website will contain, CSS controls how information technology volition await. JavaScript and its frameworks make your website interactive – responsive to a user'south actions. Developers use JavaScript frameworks such as Angular and React to make the content on the folio dynamic.
Business organisation layer
This layer, too called Business Logic or Domain Logic or Application Layer, accepts user requests from the browser, processes them, and determines the routes through which the data volition exist accessed. The workflows by which the data and requests travel through the back end are encoded in a business concern layer. For example, if your application is a hotel booking website, business logic will be responsible for the sequence of events a traveler will get through when booking a room.
Although business rules can be a manifestation of the business logic, they are not the same. Sometimes business organization rules are extracted and managed separately, using a Business Rules Management System, every bit nosotros discussed in our article on back part systems.
Persistence layer
Also called the storage or information access layer, the persistance layer is a centralized location that receives all information calls and provides access to the persistent storage of an awarding. The persistence layer is closely continued to the business layer, so the logic knows which database to talk to and the data retrieving process is more optimized.
The information storage infrastructure includes a server and a Database Management System, software to communicate with the database itself, applications, and user interfaces to obtain data and parse it. Typically you tin can store your data either in owned hardware servers or in the cloud – significant, that you purchase data middle management and maintenance services while accessing your storage virtually. Using the services of deject engineering science providers such as Amazon, Google, or Microsoft, you can utilize Infrastructure-as-a-Service, Platform-every bit-a-Service, or serverless approaches to cloud management.
In that location are also components that usually exist in all web applications simply are separated from the principal layers:
Cross-cutting code. This component handles other application concerns such as communications, operational management, and security. It affects all parts of the system simply should never mix with them.
Tertiary-party integrations. Payment gateways, social logins, GDSs in travel websites are all integrations continued to the application'southward back end via pieces of code chosen APIs. They permit your software to source data from other software and widen your functionality without coding it from scratch. Read how APIs work in our dedicated article.
Let's meet how the iii-tier architecture is implemented in different types of web applications.
Example #1. Dynamic web pages, SPAs, and MPAs
The awarding's front end can serve either static or dynamic content. In most cases, it's a combination of both. Static Web Pages exist on a server as they are and contain information that doesn't modify. Dynamic Web Pages change information every twenty-four hours or in response to a user's request – call back of whatever news website or your Twitter feed. The combination of dynamic and static content makes up a web application. The simplest example of a web application with dynamic content is a Single Page Application.
Unmarried Page Applications
The primary purpose of SPAs is the ability to access all information from a single HTML page. Having moved the application logic to the customer-side and using server-side only equally data storage, developers can make the website run faster and ease the load off the server. The front end terminate, aside from HTML and CSS, is written on a single framework, which dynamically generates content and transmits it to a user (think of a Facebook feed or your Gmail). Dependencies between components are tight. This means that making changes to ane of the UX or UI elements necessitates rewriting the whole front code.
Since SPAs move the logic to the client-side, they take to be written using client-side scripting. If you lot're using customer-side scripting technologies, you're basically building templates, so when a user requests content, a server simply transmits this information back to the browser, which renders it according to the templates. This significantly reduces the server load, as opposed to server-side scripting. The cadre technology of client-side scripting is JavaScript. Forth with its many frameworks, this language allows creation of both small and robust applications.

Single Page Awarding architecture
When the part of the server is reduced to information services, this is sometimes called thin server architecture.
We tin can't talk about SPAs without mentioning the more traditional model – Multi-Page Applications.
Multi-Page Applications
In Multi-Folio Applications, some content requests need a whole new web page to be retrieved from the server. These are massive applications with multi-layered UI. AJAX technology solves the difficulties of complex applications transferring a huge amount of data between server and browser, refreshing just selective elements of the application. At the same time, the given arroyo brings more complexity to the table being more difficult to develop every bit compared to that of the SPA.
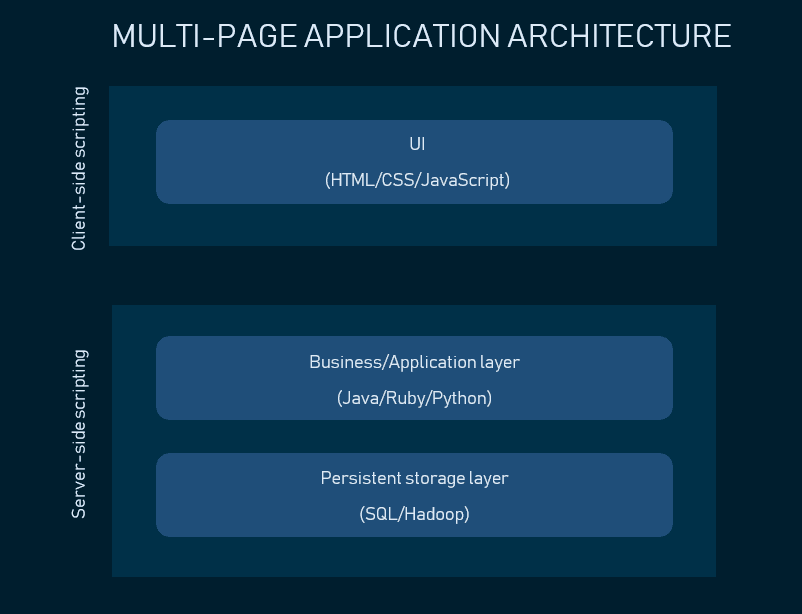
MPA compages
As opposed to the SPA'south client-side scripting, traditional applications are written using both client- and server-side languages. Server-side scripting means that all operations are performed on the server's end, then when you request content, it processes the script, retrieves data from the storage and chooses the content to display. Server-scripting languages you should be familiar with include PHP, Java, Python, Ruby, C#, and more.
Example #two. Enterprise applications
Enterprise application is a highly customizable software that's adult specifically for the needs of a particular arrangement. It usually has several business-oriented tools integrated under a single interface. Enterprise systems are likewise direct wired into the visitor's existing workflow. They are robust, requite access to a lot of users simultaneously, and share interfaces with various other enterprise tools. If y'all desire to know more about the process of developing an enterprise architecture, check out article.
The two main distinctions enterprise application architecture has from a regular spider web awarding is the add-on of another layer to the archetype pattern – the service layer.
The service layer is another abstraction between Presentation and Business Logic. It's an integration gateway that allows other software to access your business logic and resources without interacting with those resources directly. It works by passing messages through a separate interface and works like an API.
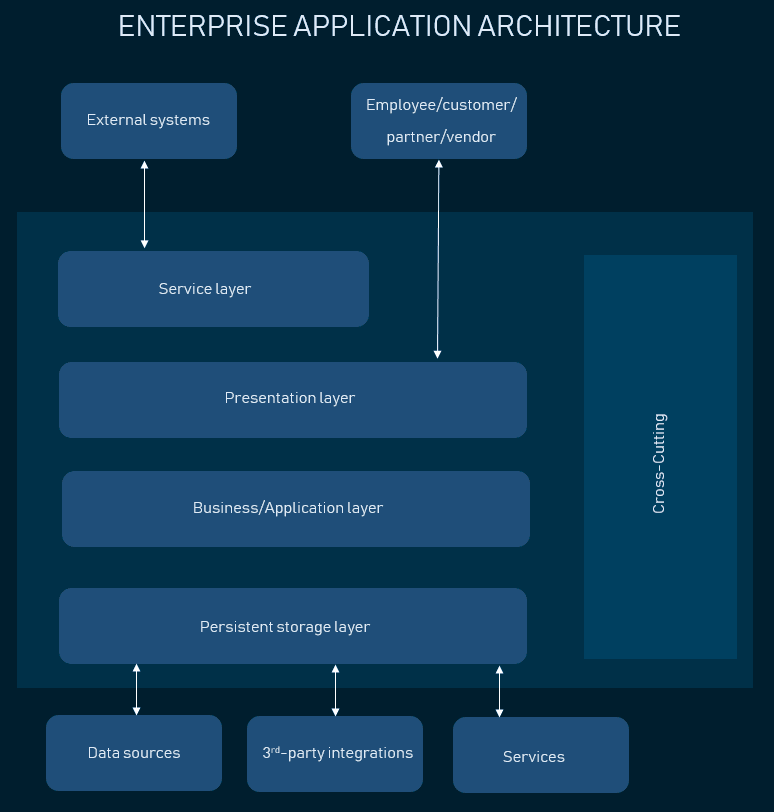
Enterprise awarding architecture
Autonomously from an extra layer, enterprise applications accept admission to data sources from other applications in an organization, making it a network of software solutions, connected by APIs. As well, there are more than groups of users who have access to dissimilar functional components – they can be business organisation partners, clients, admins, and several groups of staff. Sometimes the presentation tiers are divide for all of them, so you lot can deploy the awarding as intranet or extranet.
To conclude
This, hopefully, sheds some low-cal on the backstage of edifice modern websites. In this article, we dipped our toes into the complicated field of study of software engineering. If this wasn't enough for you lot, feel free to roam around our blog a bit more and specifically explore the post-obit articles.
The Good and the Bad of JavaScript Full Stack Development
Technical Documentation in Software Development: Types, Best Practices, and Tools
How to Employ Open Source Software: Features, Principal Software Types, and Selection Advice
What Is Web ;layer Buisness Logic Layer And Data Layer,
Source: https://www.altexsoft.com/blog/engineering/web-application-architecture-how-the-web-works/
Posted by: rothblead1998.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Web ;layer Buisness Logic Layer And Data Layer"
Post a Comment